ASTM International, formerly known as the American Society for Testing and Materials, is a non-profit international organization dedicated to developing and publishing technical standards. Established in 1898 in the United States, ASTM initially focused on addressing quality and standardization issues in the railway industry. Over time, the organization expanded its scope and has become one of the leading standard-setting bodies worldwide, with over 12,000 active standards adopted in more than 140 countries, supported by contributions from over 30,000 experts.
Through this article, you will gain a deeper understanding of ASTM’s indispensable role in shaping and advancing modern industries, highlighting the value of adhering to these standards in manufacturing and business operations.
1. Definition of ASTM Standards
ASTM standards are technical documents developed by ASTM International, encompassing specific requirements, testing methods, guidelines, and technical definitions. These standards ensure consistency and precision in manufacturing, testing, and the use of products, materials, and services.
Key features of ASTM standards include:
- Wide Applicability: Used across various industries such as construction, oil and gas, healthcare, and aerospace.
- Continuous Updates: Adjusted regularly to align with technological advancements and market needs.
- Transparent Development Process: Created through the consensus of leading experts, organizations, and businesses.

2. Importance of ASTM Standards
2.1. Ensuring quality
ASTM standards establish specific technical criteria, covering everything from raw materials to production processes and testing methods, ensuring products meet requirements for durability, safety, and performance. This minimizes deviations or defects during production and builds trust with customers.
For example, when a company complies with ASTM standards, its products are more likely to pass quality inspections, reducing risks of returns or contract penalties due to technical issues.
2.2. Enhancing competitiveness
Compliance with ASTM standards boosts international credibility, enabling products to be accepted in multiple markets. This expands business opportunities and provides a competitive edge over non-compliant competitors.
For instance, a steel manufacturer adhering to ASTM A36 (carbon steel) can easily supply materials to both domestic and international projects, as this standard is widely recognized in the construction industry. Similarly, adopting ASTM D638—a standard detailing tensile strength testing for plastics—helps plastic manufacturers gain trust when entering export markets.
Moreover, having ASTM-certified products reduces marketing costs and simplifies quality validation, thanks to the global recognition of these standards.
2.3. Promoting international collaboration
ASTM standards serve as a “common language” in engineering, facilitating communication and exchanges among businesses from different countries. This is particularly critical in industries requiring cross-border compatibility and efficiency, such as energy, aerospace, and healthcare.
For example, ASTM D445 (kinematic viscosity) ensures that lubricants produced by manufacturers in the Middle East can be used in equipment operated by companies in North America or Europe without further adjustments.
Standardization through ASTM minimizes costs and delays by eliminating the need for product redesigns or re-testing in international transactions, enabling businesses to participate in global supply chains seamlessly.
2.4. Protecting consumers
ASTM standards impose stringent safety and quality requirements, safeguarding consumer rights by preventing the circulation of substandard or hazardous products.
3. Popular ASTM Standards and Applications
ASTM International has developed thousands of standards applied in manufacturing and industrial fields. Below are some representative standards:
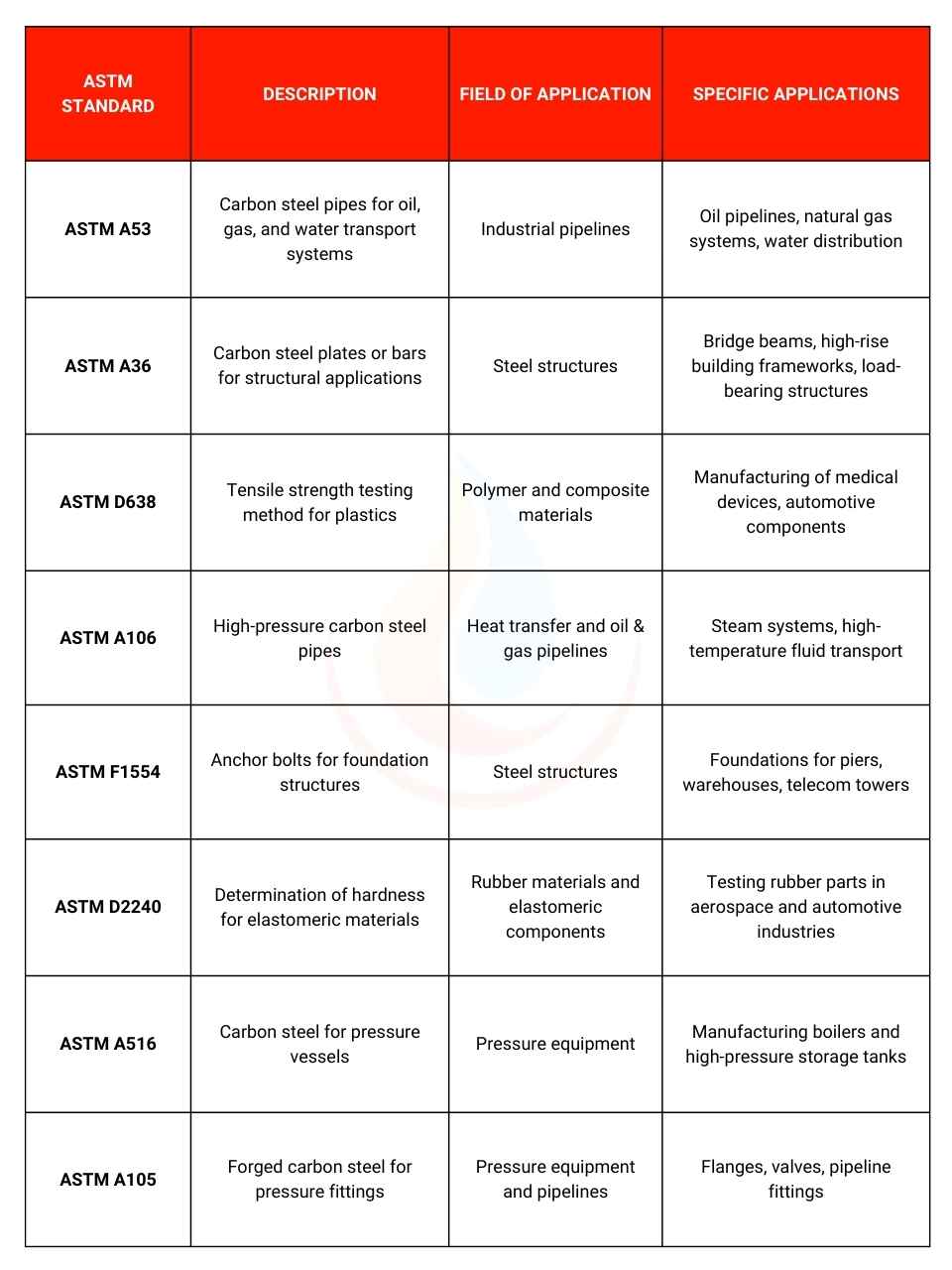
ASTM standards not only ensure that products meet technical requirements but also enhance reliability and efficiency in production and operation. This helps businesses improve their competitiveness in the global market while meeting stringent safety requirements.
Currently, ASTM International has developed over 12,000 technical standards applied worldwide. These standards are divided into 15 main categories. This diversity helps ASTM become one of the leading organizations in technical standard development, catering to the specialized needs of each industry.
4. Challenges in applying ASTM Standards
4.1. Cost
Cost is one of the major challenges in applying ASTM standards, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises.
To achieve certification, businesses need to invest in purchasing official documents from ASTM, upgrading facilities, testing equipment, and implementing inspection processes. These investments can impose a significant financial burden, affecting the company’s cash flow, especially when these costs are not immediately recoverable.
For example, a steel manufacturing company may need to invest in advanced quality testing systems, such as material tensile testing equipment, to comply with ASTM A36 for construction steel.
Additionally, the costs of certification and maintaining these standards must be considered, particularly since ASTM standards require periodic evaluations, which further increase the financial burden on businesses. This can cause companies with limited financial resources to struggle with applying these standards.

4.2. Time
The certification process is often lengthy, ranging from checking and evaluating production processes, inspecting product quality to official paperwork and certification procedures. This process not only takes time but can also impact the production and business schedules of companies.
This is particularly true for businesses in the construction or material manufacturing sectors, where meeting ASTM standards requires testing the quality of materials such as cement, steel, or concrete.
For example, a cement manufacturing company needs several months to test and certify their product according to ASTM C150 for Portland cement. During this time, the company may be unable to deliver certified products, reducing its competitiveness in the market and affecting production plans. The long certification period can also disrupt production activities, making it impossible for the business to fulfill orders on time.
4.3. Workforce
Workforce is another critical factor when applying ASTM standards. To comply with these standards, companies need a highly skilled workforce that understands technical requirements and implementation processes of ASTM standards.
However, finding and training this workforce is not easy. Engineers and specialists need in-depth knowledge of specific standards and must be familiar with strict regulations in areas such as structural design, materials, and production processes.
For example, the team of engineers designing pressure pipelines needs training to master ASTM A105 for pressure steel pipes. However, training and maintaining a highly specialized workforce is a lengthy and costly process, which not every company can afford. A shortage of skilled personnel can lead to non-compliance with standards, affecting product quality and safety in production.
4.4. Access to information
Access to information is also a significant challenge when applying ASTM standards. ASTM standards typically require businesses to purchase official documents from the organization, which can be quite expensive.
This creates difficulties for small or newly established businesses, as the cost of purchasing these documents can be a significant investment, especially when they are uncertain about the effectiveness of using these documents in production.
Moreover, these standards require employees to have specialized knowledge to accurately understand and apply them. Small businesses or those without sufficient resources may struggle to train employees or obtain specific information.
For instance, a medical device manufacturing company needs to study ASTM F899 to ensure the quality of stainless steel materials. However, accessing these documents and fully understanding the technical requirements of the standards can be challenging due to cost and lack of skilled personnel.

5. Solutions
5.1. Financial support from Government and Organizations
Financial support from the government and organizations can help reduce the cost burden for businesses when complying with ASTM standards. The government can offer favorable loan programs or grants so that businesses can invest in quality control systems and necessary equipment to achieve certification.
This not only helps businesses access new technologies but also minimizes the initial costs of applying ASTM standards. Additionally, the government can encourage collaboration between large and small businesses to share costs and infrastructure. Small companies can cooperate with larger corporations to take advantage of existing resources, thus reducing initial investment costs.
Such forms of financial support can enhance the competitiveness of businesses and promote industrial development in the region.
5.2. Reducing time with technology
Using modern technology is an effective solution to shorten the certification time for ASTM standards. The application of automated testing software can speed up the testing and analysis process, thereby reducing the time needed for certification.
Non-destructive testing (NDT) systems, such as magnetic particle inspection, are a prime example. These systems enable fast material quality checks without damaging the product, helping businesses meet the requirements of ASTM E1444 standards.

Using these technologies helps minimize production downtime, increase productivity, and improve work efficiency. Technology not only accelerates the certification process but also supports businesses in maintaining consistent and reliable product quality, thereby enhancing their competitiveness in the global market.
5.3. Training and Developing Human Resources
Training and developing human resources is a key factor in successfully applying ASTM standards. To ensure that employees understand and comply with these standards, businesses need to invest in specialized technical training programs.
These programs can collaborate with universities and research institutes to develop a workforce that is knowledgeable and capable of understanding international technical standards. ASTM experts can also be invited to organize industry-specific workshops to help employees grasp the specific requirements of standards in various fields.
This not only enhances employee capabilities but also ensures that production and testing processes meet the highest quality standards. Furthermore, human resource training is an important step in minimizing errors during production and ensuring that the business meets the stringent requirements of international standards.
5.4. Building an Accessible Information Repository
Building an accessible information repository is an important solution to help businesses reduce difficulties in accessing and understanding ASTM standards. Developing digital libraries or online platforms that provide official ASTM reference materials will make it easier for businesses to access necessary documents.
These platforms can offer information about specific standards, how to apply them, and detailed technical requirements. Additionally, encouraging the translation and dissemination of ASTM documents in local languages is also a helpful solution, allowing businesses to easily access and better understand the standards without facing language barriers. This will facilitate the adoption of international standards in developing countries, contributing to improving the quality of products and services offered by businesses.
