Detailed drawings are a crucial part of the design and production process for technical products. They are commonly used in industries such as mechanical engineering, electronics, and construction. Detailed drawings include specific technical specifications and dimensions of the product, helping those involved in the production process to understand the product requirements better. Without accurate and comprehensive detailed drawings, errors in production can occur, leading to significant time and financial losses for the company. Therefore, detailed drawings are considered an essential factor in the design and production of technical products.
1. What are detailed drawings?
Detailed drawings are an indispensable part of the product design and manufacturing process, especially in industries like mechanical engineering, construction, and manufacturing. These drawings are specific and detailed versions derived from the overall design drawings, containing crucial information about dimensions, shapes, materials, and technical requirements of each product detail. Detailed drawings ensure that every aspect of the product is manufactured according to the established technical and safety standards.
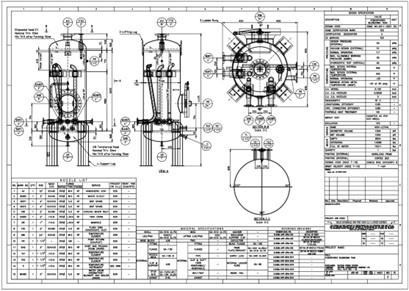
1.1. Contents of Detailed Drawings
Detailed drawings serve as critical documents in the production process, helping the implementers understand each aspect of the product and ensuring compliance with technological and safety requirements. Information typically included in detailed drawings comprises:
- Dimensions and shapes: Specific measurements of length, width, height, and angles of the detail.
- Materials: The type of material used to manufacture the detail, such as steel, aluminum, plastic, etc.
- Connections and assembly: Methods of connecting details, such as welding, bolting, or joining.
- Other technical requirements: Including tolerances, surface finishes, and special instructions related to the manufacturing process.
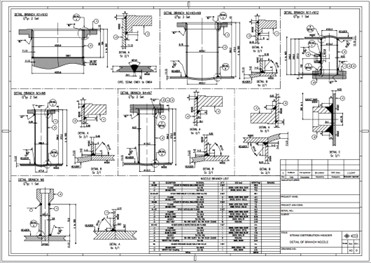
Welded joint detailed drawing designed by Prebecc
1.2. Designing Detailed Drawings Process
This process includes several steps, from initial information gathering to the production of the final product. Here is a detailed analysis of each step:
Step 1: Gather information about the product to understand its requirements and usage. The designer can then determine the necessary elements to meet the user’s needs. During this stage, the designer should:
- Research documents and information related to the product.
- Interview and discuss with stakeholders, such as customers, design engineers, and technical experts.
- Collect initial technical specifications, including dimensions, materials, working conditions, and standards to comply with.
Step 2: Define technical and safety requirements to set the technical and safety standards needed during production.
- Identify industry standards relevant to the product.
- Consider requirements for durability, load-bearing capacity, and product stability.
- Assess safety factors, including potential risks and preventive measures.
Step 3: Design detailed drawings with complete information on the dimensions, shapes, and materials of each product detail.
- Use specialized design software such as CAD (Computer-Aided Design) to create technical drawings.
- Clearly indicate the dimensions, shapes, and materials of each detail.
- Include technical instructions, such as tolerances, surface finishes, and assembly methods.
Step 4: Review and approve the drawing before production.
- Conduct internal reviews of the drawing by engineers and technical experts.
- Compare the drawing against the defined technical and safety standards.
- Make necessary corrections and adjustments to the drawing.
- Approve the final drawing to be ready for the production process.
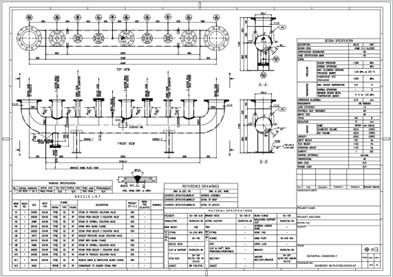
Comprehensive detailed drawing
2. Common Types of Detailed Drawings
Detailed drawings can be classified in various ways depending on their usage and project requirements. Some common types of detailed drawings include:
- Technical drawings: Show specific technical parameters of details.
- Layout drawings: Display details on a flat plane, making it easier to visualize and assemble.
- 3D drawings: Provide a three-dimensional view of the details, helping viewers understand the overall structure and shape better.

3D drawing of a pressure device in the finalization process.
3. Advantages of Detailed Drawings
Detailed drawings play a vital and irreplaceable role in the product design and production process. With numerous outstanding benefits, detailed drawings ensure accuracy, cost savings, and product quality enhancement. Here are five prominent advantages of using detailed drawings in production:
3.1. Ensuring Production Accuracy
Detailed drawings provide specific and clear information about the product, from dimensions and shapes to technical requirements. This helps engineers and workers execute the production process according to the established standards, minimizing errors and ensuring the final product meets the design requirements. This accuracy is especially crucial in industries requiring high precision, such as aerospace, automotive, and medical sectors.
3.2. Saving Time and Costs
Using detailed drawings in the production process helps optimize the execution steps, reducing the time needed to complete the product. When all details are planned and clearly defined, the production process will run smoothly and efficiently, avoiding errors and rework. This not only saves time but also minimizes production costs, bringing significant economic benefits to the business.
3.3. Enhancing Accuracy and Safety
Detailed drawings ensure that each part of the product is manufactured with the highest accuracy, thereby increasing safety when the product is used. In industries requiring strict safety standards, such as construction and transportation, ensuring technical details through drawings is a key factor in preventing risks and accidents.
3.4. Maintaining Consistency Among Parts
Detailed drawings provide specific information about each product part and how they fit together. This ensures consistency and uniformity in the production process, helping parts work together seamlessly and efficiently. This consistency is crucial to ensure the product’s stable and long-term operation.
3.5. Improving Product Quality
Finally, detailed drawings significantly contribute to enhancing product quality. When the production process is tightly controlled based on detailed drawing information, the products created will meet higher technical and aesthetic standards. The accuracy and quality of the product not only meet customer demands but also enhance the business’s reputation and position in the market.
4. Distinguishing Detailed Drawings and Assembly Drawings in the Boiler Industry
In the boiler industry, two common types of drawings used are detailed drawings and assembly drawings. While they share many similarities, there are also crucial differences that need to be understood to ensure a smooth production and assembly process. Here is a detailed analysis of the similarities and differences between these two types of drawings:
Similarities:
- Both detailed drawings and assembly drawings belong to technical drawings, containing representations, dimensions, and title blocks to provide specific product information.
- Reading both types of drawings follows a certain sequence, helping readers easily grasp the information.
- When reading both types of drawings, readers will know the shape, dimensions of parts or products, and the accompanying technical requirements.
Khác nhau:
|
Detailed Drawings |
Assembly Drawings |
|
| Assembly Drawings | Only provide information about a specific detail of the product, including its shape, dimensions, and technical requirements. | Provide information about the product assembled from various details. They help readers understand the overall shape, structure, and relative positions of the product’s details. |
| Purpose | Used to manufacture and inspect a specific detail of the product, ensuring it meets the established technical standards. | Used to understand how to assemble details together, ensuring parts fit accurately in their defined positions. |
| Technical elements | Do not include a parts list but will have specific technical requirements for that detail, such as materials, tolerances, and required technical standards. | Usually include a parts list, listing all components needed to assemble the complete product. |
